Selected Projects
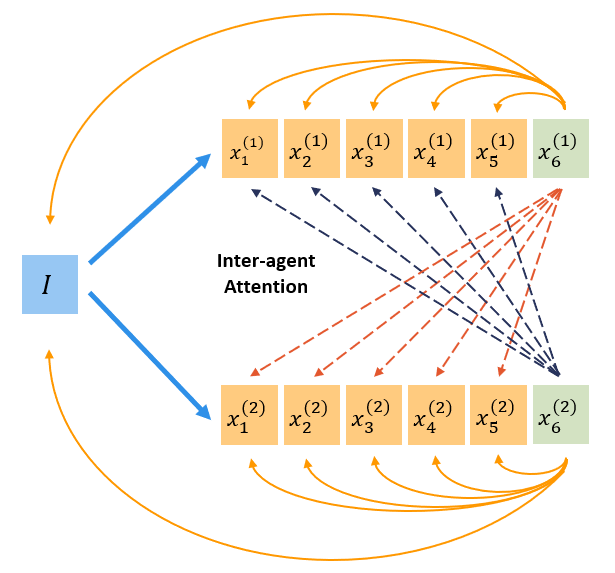
Group Think: Collaborative Reasoning in Large Language Models
We introduce Group Think, a collaborative reasoning framework for large language models in which multiple reasoning trajectories interact during generation. Inspired by ideas from communication theory, this approach allows concurrent reasoning paths to exchange information at the token level, leading to emergent cooperative behaviour. Group Think improves reasoning accuracy without increasing inference latency and allows for efficient utilization of idle computational resources, making it especially suitable for edge inference, where very small batch sizes often underutilize local GPUs.
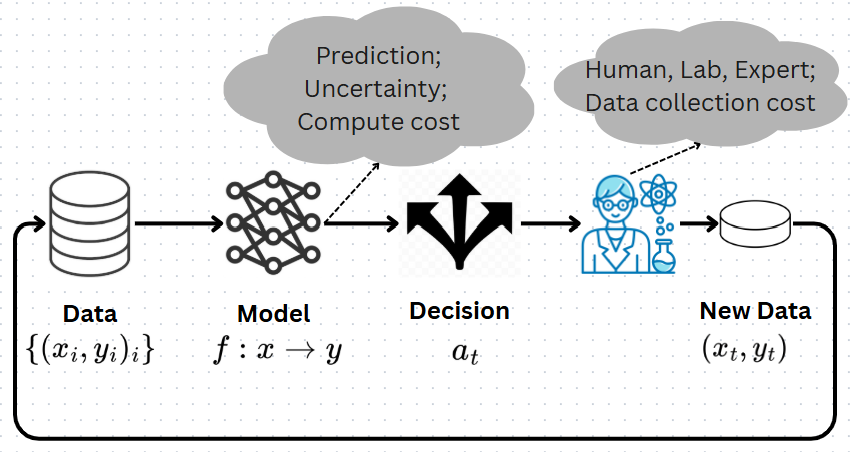
Human-in-the-Loop Learning
Many real-world decision-making problems rely on human input rather than precise numerical feedback, such as preferences, comparisons, or rankings. This line of work studies how learning algorithms can efficiently incorporate human feedback while properly accounting for uncertainty. We develop principled methods for Bayesian optimisation from human preferences, showing that learning from comparisons can be nearly as effective as learning from numerical rewards. Our results support the use of preference-based optimisation in interactive and human-guided learning settings.

AI for Communication Systems
Traditional machine-learning approaches for communication systems are typically task-specific and require large amounts of labelled data. In this project, we take steps toward a foundation model for communication systems, trained on large-scale, unlabeled wireless data. We address key challenges such as representing complex signals, handling multimodal inputs, and learning from data with varying structures. The resulting models demonstrate the ability to support multiple downstream communication tasks from shared representations, moving toward more general and adaptive AI-driven communication systems.

Kernel-based Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement Learning (RL) has shown strong empirical performance in complex environments, but existing theory often focuses on small state–action spaces or simple function classes. To address large-scale problems with richer value functions, this work develops RL algorithms based on kernel methods. We introduce kernel-based learning and exploration strategies that achieve order-optimal regret guarantees for a broad class of kernels. The results establish statistically efficient decision-making in settings ranging from finite-horizon to average-reward Markov decision processes.
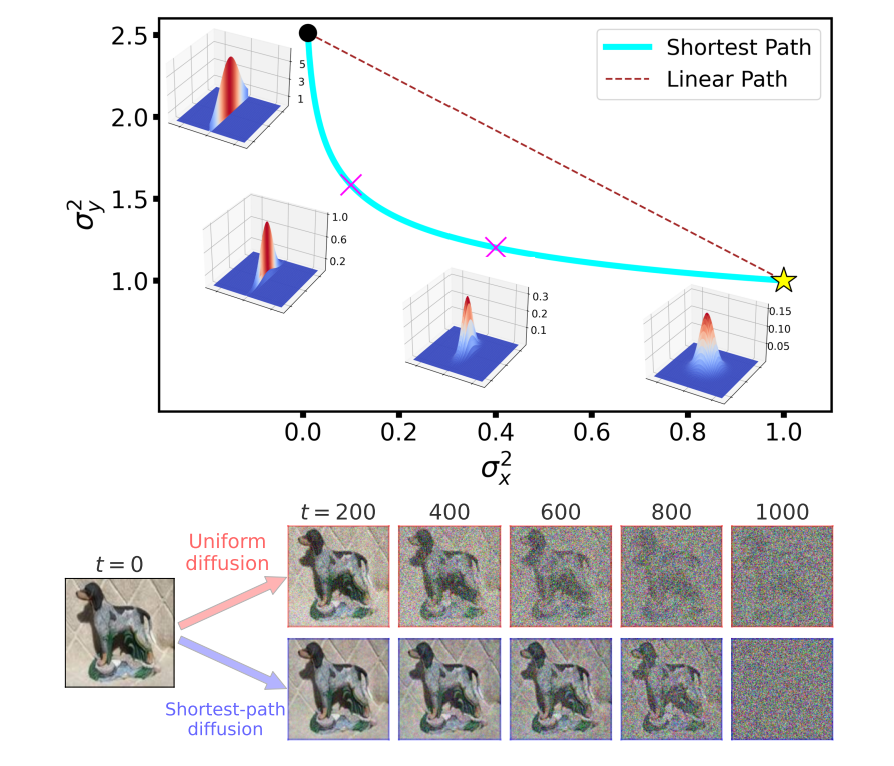
Shortest Path Diffusion
Denoising diffusion models have achieved significant success in image generation by gradually adding and removing noise. We introduce Shortest Path Diffusion (SPD), a framework that perturbs data along the shortest path between the data distribution and noise. By defining distances using the Fisher metric in the space of probability distributions, SPD uniquely determines the structure of the diffusion process. The method outperforms strong baselines while requiring no hyperparameter tuning.
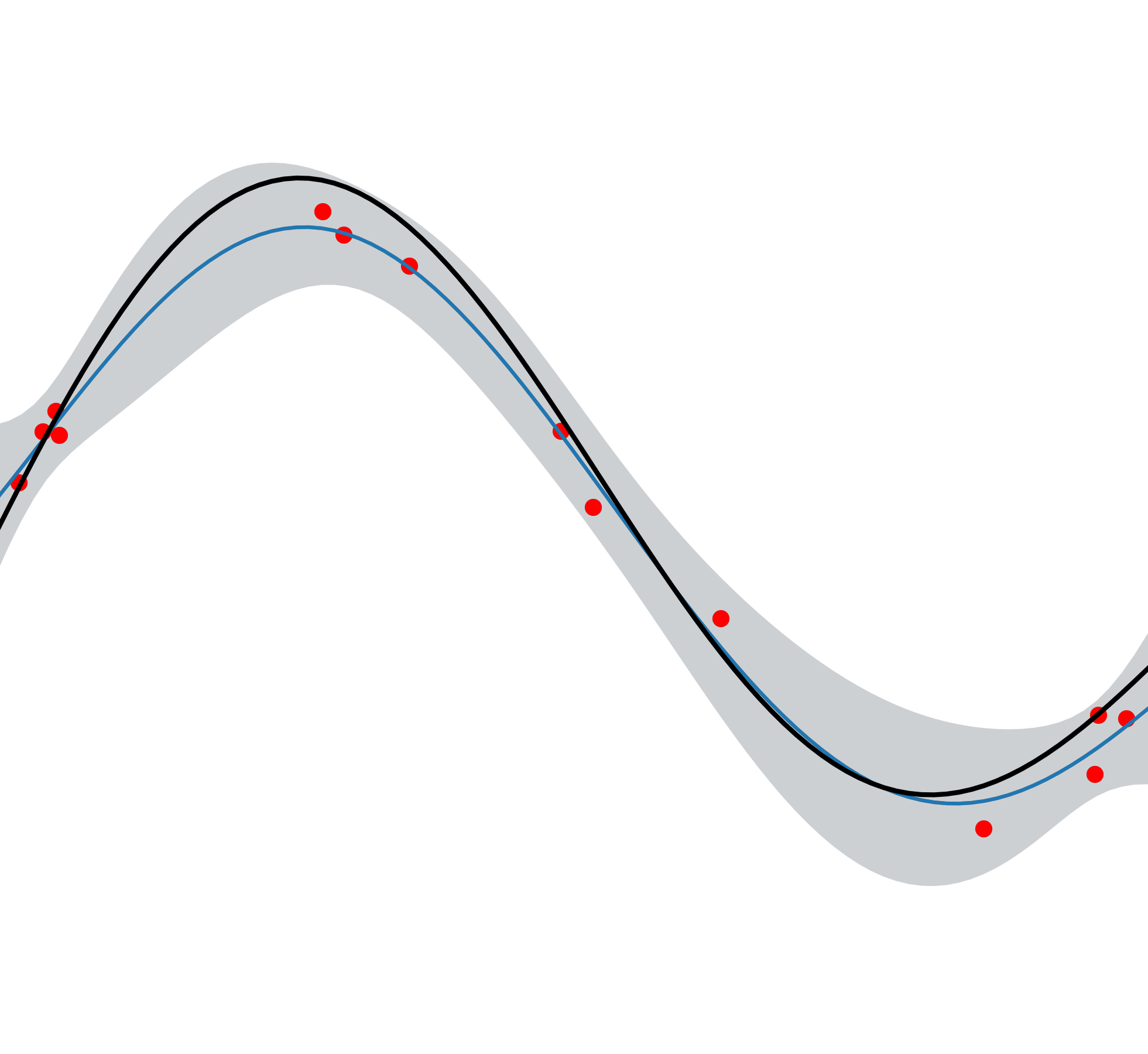
Convergence Rates of Nyström Method and SVGP
Kernel ridge regression and Gaussian processes are widely used for regression and optimisation, but their computational cost can be prohibitive. Sparse approximation methods such as the Nyström method and sparse variational Gaussian processes (SVGP) reduce these costs, yet their accuracy guarantees have been limited. In collaboration with Jonathan Scarlett (National University of Singapore), we derive new confidence intervals for these approximations through improved interpretations of surrogate posterior variance, leading to tighter performance bounds for both regression and Bayesian optimisation.
Wireless Channel Modelling with Diffusion Models
Accurate channel models are essential for designing and evaluating wireless systems, yet traditional approaches struggle to capture real-world complexity. We introduce generative diffusion models for wireless channel modelling and sampling. Compared to GAN-based methods, diffusion models offer more stable training and generate diverse, high-fidelity channel samples. The framework also supports transfer learning, enabling realistic channel modelling from limited real-world data.